MUSAR – Data Fusion & Smart Automatic Classification of Satellite Multisensor/Multiband SAR and Optical Data
In 2022, the project ‘MUSAR – Data Fusion & Smart Automatic Classification of Satellite Multisensor/Multiband SAR and Optical Data’, financed by the Italian Space Agency, was concluded, among the research projects with the subject ‘STUDY OF NEW METHODS AND TECHNIQUES BASED ON THE USE OF MULTIMISSION/MULTIFREQUENCY SAR DATA’.
The project, started in May 2021, was carried out by NHAZCA in collaboration with the Research Centre “CERI – Centro di Previsione e Prevenzione dei Rischi Geologici” of the Sapienza University of Rome and its main objective was the development of new algorithms based on Data Fusion and Machine Learning techniques for the automatic classification and analysis of geohazards.
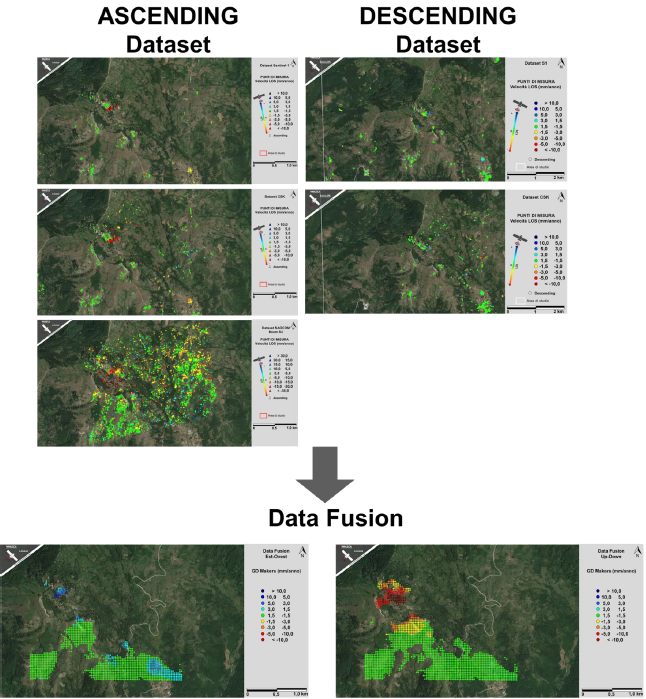
The proposal aims to integrate the SAR multi-sensor/multi-band data offered by the following satellite missions: Sentinel-1 in C-band of the Copernicus initiative, the COSMO-SkyMed constellation in X-band of the ASI and the new Italian-Argentine system SIASGE (Sistema Italo-Argentino di Satelliti per la Gestione delle Emergenze), with two SAOCOM satellites operating in L-band.
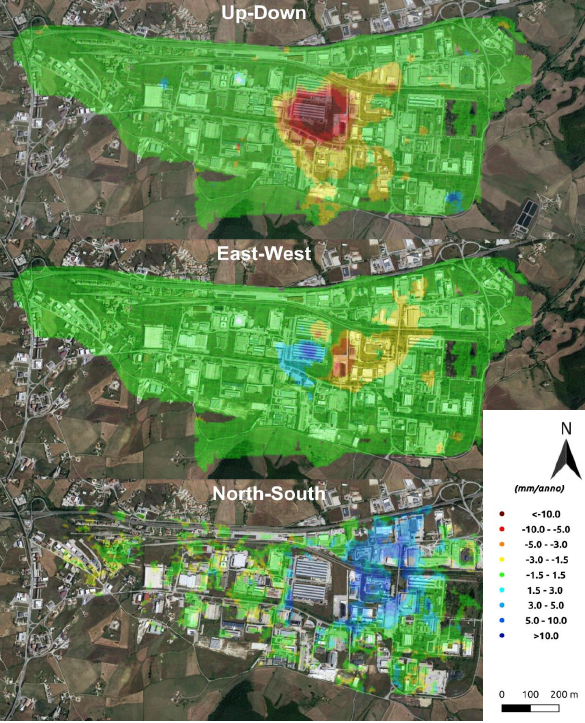
The data fusion method was implemented in an area of the Basilicata Region, South Italy, and was tested and validated using geological and geomorphological indicators to verify the correspondence between PSI and synthetic data.
Regarding the Data Fusion line, it was demonstrated how, through the implemented model, it is possible to integrate interferometric measurements and displacement maps obtained with Digital Image Correlation (DIC) techniques. Furthermore, it was possible to estimate the North-South displacement component through integration of interferometric data from different satellite missions.
As for machine learning methods for the classification of deformation processes acting on the analysis area, the necessary practices for the application of the method were defined and developed. In particular, the procedures for implementing a Dynamic Graph Convolutional Neural Network (DGCNN), i.e. a deep neural network characterised by high algorithmic complexity, were developed.